Exercise, as defined by Carl Caspersen from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, is described as physical activity that is planned, structured, repetitive, and purposive in the sense that improvement or maintenance of one or more components of physical fitness is the objective.
According to a 1985 study titled ‘Physical activity, exercise, and physical fitness: definitions and distinctions for health-related research,’ the primary goal of exercise is to enhance or maintain the five health-related components of physical fitness: cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular endurance, muscular strength, body composition, and flexibility.
In 2019, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that 19.3 percent of the U.S. population participated in exercise and sports daily with the intention of improving or maintaining physical fitness. Among the preferred exercise methods, aerobic exercise stands out, with the exercise bike being particularly popular, drawing in 6.27 million enthusiasts.
What is the definition of the exercise?
Exercise is an organized, methodical, and consistent physical activity, involving a range of movements often facilitated by machines or other apparatuses, as per Caspersen et al. (1985). During exercise, energy is expended up to and beyond 120 kJ min−1 (2 kW), equivalent to an oxygen uptake of 6 liters min−1, compared with resting rates of approximately 5 kJ min−1 (83 W), equivalent to an oxygen uptake of 0.25 liters min−1.
Physical activity, on the other hand, as defined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, is described as any bodily movement produced by skeletal muscles that result in energy expenditure. This implies any movement, passive or active, that uses energy.
What is the definition of aerobic exercise?
Aerobic exercise is defined as any activity that involves using large muscle groups, can be sustained continuously, and has a rhythmic nature, according to the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM),
During aerobic exercise, the muscles rely on aerobic metabolism to extract energy from amino acids, carbohydrates, and fatty acids in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Examples of aerobic exercise include cycling, dancing, hiking, jogging/long-distance running, swimming, and walking, as shown in this graph.

What is the definition of anaerobic exercise?
According to the ACSM, anaerobic exercise is the intense physical activity of a short duration that relies on energy sources within the muscles and does not require inhaled oxygen for energy.
Unlike aerobic exercise, which produces ATP through oxygen use, anaerobic exercise relies on glycolysis and fermentation, resulting in the production of less ATP and the buildup of lactic acid.
Examples of anaerobic exercises include strength and resistance training, weight training, functional training, eccentric training, interval training, sprinting, high-intensity interval training, and power-lifting, which primarily activates fast twitch muscles, as illustrated in this graph.

What are the different types of exercise?
There are various forms of exercise, including strength training, HIIT, pilates, yoga, CrossFit, bodybuilding, rowing, circuit training, and martial arts. However, when categorizing them broadly, there are only four main types of exercise such as endurance, strength, balance, and flexibility.
Although the National Institute on Aging (NIA) identifies four main types of exercise—endurance, strength, stretching, and balance—the following list shows 15 distinct forms and subtypes of these categories.
- Aerobic exercise
- Walking exercise
- Hiking exercise
- Running exercise
- Rowing exercise
- Swimming exercise
- Cycling exercise
- Anaerobic exercise
- HIIT exercise
- Strength exercise
- Calisthenics exercise
- Pilates exercise
- Yoga exercise
- Stretching exercise
- Balance exercise
What are the different types of gym exercises?
The list of gym exercises is shown below.
- Deadlifts
- Bench press
- Overhead press
- Bicep curls
- Tricep dips
- Leg press
- Calf raises
- Pull-ups
- Seated row
- Lat pull-downs
- Dumbbell flyes
- Cable cross-overs
- Leg curls
- Leg extensions
What are common myths about gym exercises?
According to a 2005 study by Todd M Manini from Syracuse University, common myths, and misconceptions about gym exercises among older adults include the beliefs that lifting heavy weights will make women bulky, the number on the scale is always an accurate indicator of weight loss, ab workouts alone will result in a six-pack, sweating is an accurate indicator of workout intensity, and “no pain, no gain”.
These misconceptions highlight the need for better education and dissemination of accurate information about the benefits and recommendations of strength exercise protocols.
What’s the difference between gym exercises and bodyweight exercises?
The difference between gym exercises and bodyweight exercises, according to a 2018 study by Fernanda Maria Martins from the Federal University of Triângulo Mineiro (UFTM), can be understood as follows.
- Intensity and Resistance: Gym exercises often allow for greater control over the intensity and resistance levels, as they can be easily adjusted using weights or machines. Bodyweight exercises, on the other hand, rely on the individual’s body weight to provide resistance, making it harder to adjust intensity levels.
- Convenience and Accessibility: Gym exercises require access to fitness facilities that house the necessary equipment, which may not be readily available or convenient for everyone. Bodyweight exercises can be performed at home, anywhere, anytime, as they do not require any specialized equipment.
- Variety and Exercise Selection: Gym exercises offer a wide range of exercise options and variations due to the availability of different equipment. Bodyweight exercises also offer a variety of exercises using one’s own body weight, but the range may be more limited compared to gym exercises.
- Muscle Activation: Gym exercises often target specific muscle groups and allow for isolation exercises, targeting specific muscles or muscle groups. Bodyweight exercises, on the other hand, typically engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, promoting functional movement patterns.
- Exercise Equipment: Gym exercises typically involve the use of specialized exercise equipment available in fitness facilities, such as weight machines, dumbbells, and treadmills. On the other hand, bodyweight exercises rely solely on the individual’s own body weight as resistance, requiring little to no equipment.
What are the most popular types of exercise equipment?
The most popular types of exercise equipment in the United States in 2022 were weightlifting equipment, treadmills, and resistance bands. These were the preferred pieces of home exercise equipment among consumers. The surge in popularity of home exercise equipment in 2020 was primarily due to the COVID-19 pandemic, which prompted many to invest in home fitness products due to lockdowns and restrictions.
What are the most popular types of home exercise equipment?
The most popular type of home exercise equipment in the United States as of April 2022 was associated with the brand Peloton, which was considered by 21.8% of U.S. survey participants to produce the most effective exercise equipment. The second most popular brand was Bowflex, with 13.4% of respondents voting.
What is the best exercise to lose weight?
The best exercise to lose weight, according to a 2014 study by Hye-Ryun Hong from Sungkyunkwan University, is walking. This exercise is particularly effective for reducing abdominal fat and improving insulin resistance.
A 12-week walking routine was found to effectively reduce abdominal fat, both subcutaneous and visceral. Participants walked three times a week, spending 50-70 minutes per session, and aimed to burn 400 kcal each time.
Is walking good exercise?
Yes, walking is a beneficial form of exercise that utilizes your body weight and positively impacts public health. It is recommended as a moderate-intensity physical activity and has been shown to have numerous health benefits. Its accessibility and documented advantages make it a valuable tool in promoting a healthy lifestyle and reducing chronic disease rates.
The benefits of walking are highlighted in a 2008 study by I-Min Lee from Harvard Medical School titled “The importance of walking to public health”.
What exercise burns the most calories per hour?
Running burns the most calories per hour, as per a 2012 study by Linda D Wilkin from California State University. The study showed that energy expenditure during the run was 471.03 ± 100.67 kilojoules, which was significantly higher than the 372.54 ± 78.16 kilojoules expended during the walk. However, when asked what exercise burns the most calories, the answer depends on various factors such as intensity and duration, as well as the individual’s age, gender, body composition, and fitness level.
How many calories do you burn in a day without exercise?
The number of calories an individual burns in a day without deliberate exercise ranges from 1,300 to more than 2,000, according to Christian von Loeffelholz from Jena University Hospital. However, this can vary widely based on factors such as age, gender, lean body mass, occupation, and overall activity level. On average, for those with predominantly sedentary lifestyles, BMR comprises about 60% of TEE. With the addition of NEAT and TEF, the calorie burn can increase, though the precise number is specific to each individual.
What exercises target belly fat?
The most effective exercise for targeting belly fat in females, according to a 2016 study by Chia-Hua Kuo from the University of Taipei, is high-intensity intermittent training (HIIT). This study found that HIIT is more effective in reducing abdominal fat than continuous aerobic training when both are performed with similar energy expenditure.
What exercises target back fat?
The exercises that target back fat are listed below.
- Dead bug exercise
- Push-up exercise
- Sit-up exercise
- Squat exercise
- Plank exercise
- Bird dog exercise
- Superman exercise
- Burpee exercise
- Bridge exercise
- Fire hydrant exercise
- Russian twist exercise
- Mountain climber exercise
- Clamshell exercise
- Lunges exercise
- Crunches exercise
- Pelvic tilt exercise
- Glute bridge exercise
What is the purpose of exercise?
The purpose of exercise is to engage in physical activity that improves or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness. Physical fitness is a set of attributes that people have or achieve that relates to the ability to perform physical activity. It is defined as the ability to carry out daily tasks with vigor and alertness, without undue fatigue, and with ample energy to enjoy leisure-time pursuits and meet unforeseen emergencies.
Physical fitness is a multi-dimensional concept and includes the following measurable components.
- Cardiorespiratory Fitness: A 2020 study by Geetha Raghuveer from Children’s Mercy Hospital defines cardiorespiratory fitness as the ability of the circulatory and respiratory systems to supply oxygen to the skeletal muscles’ mitochondria that are needed for energy production during physical activity. It’s an important health marker, with low or unhealthy levels of CRF being a strong independent predictor of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and all-cause mortality in adults.
- Muscular Endurance: A 2001 study by Robert T Kell from the University of Alberta defines muscular endurance as the ability of a muscle or muscle group to perform repeated contractions against a load for an extended period of time without experiencing fatigue. This ability is crucial to overall musculoskeletal fitness, and hence to overall physical health and well-being.
- Muscular Strength: Muscular strength refers to the maximum force that a muscle or group of muscles can generate against resistance at a given speed. According to a 2016 study by Timothy J Suchomel from East Stroudsburg University, greater muscular strength has been associated with the ability to perform general sports skills such as jumping, sprinting, and changing direction more effectively.
- Flexibility: Flexibility refers to the inherent properties of body tissues that determine the maximum range of motion of a joint without causing injury. It has long been considered as a major component of physical fitness by institutions like the American College of Sports Medicine.
- Body Composition: Body composition refers to the relative proportion of lean body mass (LBM) and body fat mass (BFM) within the body. Body fat estimates commonly use anthropometric measurements, including height, weight, skinfold thicknesses, body diameters, and body circumference. Another technique, Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA), is also used to estimate body composition by measuring the passage speed of a small electrical signal through the body.
This photo shows the multi-frequency segmental body composition analyzer – Tanita.

Apart from weight loss or maintenance, promoting growth and strength, and hypertrophy (building muscles) and cardiovascular health, exercise can also serve other purposes, such as enhancing athletic skills, improving overall health, and providing enjoyment.
What are the benefits of exercise?
The benefits of exercise, based on a 2014 study by Frank W. Booth from the University of Missouri, encompass a wide range of health, physical, and psychological improvements. Exercise enhances the cardiovascular and immune systems, aids in obesity control, prevents metabolic syndrome, and boosts insulin sensitivity. Physically, it leads to increased strength, bone density, and better balance. Psychologically, exercise provides stress relief and uplifts mood. However, the long-term benefits of exercise can vary based on the specific type, intensity, and duration of the exercise.
What are the benefits of exercise for lower back pain?
The benefits of exercise for those with lower back pain, as highlighted by a 2004 study by James Rainville from The Spine Center at New England Baptist Hospital, include no increased injury risk, enhanced back flexibility, and strength, a reduction in pain intensity by 10% to 50%, and decreased pain-related disability through improved well-being and altered pain perceptions.
What are the risks of not exercising?
Physical inactivity, or not exercising, significantly increases the risk of chronic diseases and can lead to a decline in both the quality and length of life, according to a 2014 study published in Comprehensive Physiology Journal.
It can cause various health issues including heart disease, diabetes, certain types of cancer, and mental health problems. Furthermore, lack of exercise accelerates biological aging and decreases physical and cognitive functions. In essence, regular exercise is crucial for maintaining good health and preventing a multitude of chronic diseases.
What are the risks of not doing pelvic floor exercises?
Not doing pelvic floor exercises, or Kegels, can lead to several risks. Neglect can result in urinary incontinence due to weakened muscles controlling urination, pelvic organ prolapse where pelvic organs may descend causing discomfort, and decreased sexual function affecting arousal and sensation. These issues can significantly impact the overall quality of life, but regular pelvic floor exercises can mitigate these risks.
What are Kegel exercises?
Kegel exercises, also known as pelvic floor muscle exercises, were first described by Arnold Kegel in 1948 as a way to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. These exercises are beneficial for both men and women and can help prevent and treat various issues such as urinary incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse, and sexual dysfunction.
What are the best kegel exercises for men?
The best Kegel exercises involve consistently strengthening the pelvic floor muscles. To perform them effectively: first, identify the pelvic floor muscles by trying to stop the flow of urine midstream; second, contract these muscles, holding for a few seconds, then relax and repeat; and third, alternate between fast and slow contractions, gradually increasing intensity and considering the use of resistance devices for enhanced effectiveness.
What are the best exercises for seniors?
The best exercises for seniors, as highlighted in a 2018 study by Jorge Camilo Mora from FIU Herbert Wertheim College of Medicine, include a combination of aerobic, muscle-strengthening, stretching, and balance activities tailored to individual abilities and health conditions. Engaging in these exercises offers numerous benefits, such as reduced risk of chronic diseases.
What are some safe chair exercises for seniors?
The safest chair exercises for seniors are listed below.
- Seated Marches
- Chair Taps (or Sit-to-Stands)
- Seated Leg Lifts
- Chair Arm Raises (or Seated Shoulder Press)
- Seated Torso Twists
- Ankle Circles
- Seated Side Leg Lifts
- Chair Knee Extensions
- Seated Forward Bends
- Chair Arm Curls
What are some fun exercises for kids?
The following are some fun exercises for kids.
- Trampoline exercise
- Donkey kicks exercise
- Wood chop exercise
- Crab walk exercise
- Bear crawl exercise
- Skipping rope exercise
- Jumping jack exercise
What are some fun ways to exercise?
Fun ways to exercise involve engaging in physical activities that not only promote health and fitness, but also provide pleasure, interest, and enjoyment to the participant, according to the American College of Sports Medicine.
Some of the fun ways to exercise include dance workouts, outdoor adventures, or group fitness classes, which often deviate from traditional routines, incorporating elements of novelty and challenge to stimulate both the body and mind. Notably, engaging in these diverse activities can also impact your heart rate, encouraging a dynamic response that further enhances the overall benefits of staying active.
What is a target exercise heart rate?
A target exercise heart rate refers to a specific range of heart rate values that individuals aim to achieve during physical activity to optimize the effectiveness of their workout. The American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) recommends using percentages of maximal oxygen consumption (VO2 max) or maximal heart rate (HRmax) as target values when developing exercise plans. For example, 55%, 70%, 85%, and 90% of HRmax can be used as indices of these respective levels of % VO2max for the general population.
What happens if your target heart rate is too high during exercise?
If your target heart rate is too high during exercise, potential consequences may arise. According to a 1995 study by Leiv Sandvik from Central Hospital of Akershus, an excessively high maximal exercise-induced heart rate is linked to a higher risk of cardiovascular mortality in healthy individuals. Additionally, surpassing the target heart rate may strain your cardiovascular system, impact physical fitness, reduce exercise tolerance, and increase the likelihood of premature cardiovascular mortality.
What is the recommended exercise duration per week?
The recommended exercise duration per week varies based on age and fitness level. According to the National Guidelines for Physical Activity, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recommends that adults engage in moderate aerobic exercises for 150-300 minutes per week or vigorous aerobic exercises for 75-150 minutes per week to receive substantial health benefits. Additionally, adults should perform muscle-strengthening exercises 2-3 times a week.
How many minutes per week should I exercise for weight loss?
The optimal frequency of exercise for weight loss depends on various factors, but guidelines from The American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) recommend a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity (PA) per week for overweight and obese adults to improve health. To achieve significant weight loss, greater amounts of PA, exceeding 250 minutes per week, have been associated with clinically meaningful results.
How do you structure your weekly exercise routine?
To effectively structure your weekly exercise routine, it’s essential to incorporate a variety of activities to meet all fitness goals and maintain motivation. Adhering to the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, your routine should encompass aerobic exercises, strength training, balance exercises, and flexibility exercises. Additionally, it’s crucial to allocate time for warm-ups and cool-downs with each workout, adjust the intensity based on your age and fitness level, and always prioritize safety to prevent injuries.
When is the optimal time for a workout?
The optimal time for a workout varies based on the type of exercise and individual preferences, as per a 2012 study by Hamdi Chtourou from the National Center of Medicine and Science in Sports (CNMSS). For anaerobic exercises, peak performances tend to occur in the late afternoon, with performance being lowest in the early morning. However, training consistently at a particular time of day can influence these diurnal rhythms.
What’s the optimal time for beginners to start exercising?
The optimal time for beginners to start exercising depends on individual preferences and daily routines. It’s essential to choose a time that ensures consistency, whether it’s morning, afternoon, or evening. Paying attention to personal energy levels and selecting a time that aligns with feeling most energetic and motivated will help beginners adhere to their exercise regimen.
What are the best exercise apps for beginners?
The following is the list of the 15 best exercise apps for beginners.
- Beachbody On Demand
- SWEAT
- CENTR by Chris Hemsworth
- Nike Training Club
- Peloton App
- Grokker
- FUTURE
- Glo
- BODY by Blogilates
- Tone It Up
- Strava
- Obé Fitness
- Fitness +
- WW Digital
- All Out Studio
What are the best exercise machines?
These are the 10 best exercise machines for weight loss.
- Tonal
- Aviron Strong Series Rower
- Sole Fitness F85 Treadmill
- CLMBR
- WalkingPad R2 Walk&Run 2IN1 Foldable Treadmill
- Mirror
- REP Fitness FT-5000 Functional Trainer
- NordicTrack S22i Studio Bike
- ProForm Pro HIIT H14 Elliptical Trainer
What machine is needed for a bench press?
The primary machine needed for a bench press exercise is a “bench press rack” or “power rack.” Additionally, you’ll need a flat bench to lie on and a barbell. Common variations and related equipment include the incline bench press, decline bench press, Smith machine for guided barbell movements, Olympic bench press station, and the seated bench press machine.
Which gyms offer the best bench press machines?
The following is the list of 10 gyms in the U.S. that has the best bench press machines.
- Life Time Fitness
- Gold’s Gym
- Anytime Fitness
- 24 Hour Fitness
- LA Fitness
- Crunch Fitness
- Pure Barre
- Blink Fitness
- Equinox Fitness Club
- Planet Fitness
Which gyms offer the best group exercise classes?
Life Time and Equinox are top-tier gyms known for their extensive range of group exercise classes, tailored to cater to diverse fitness goals and preferences. Group exercise classes refer to fitness classes or workouts that are conducted in a gym or fitness studio in a group setting, typically led by a qualified instructor.
These classes involve a structured and choreographed exercise routine that targets various aspects of fitness, such as cardiovascular endurance, strength, flexibility, and coordination.
While Life Time offers unique classes like Ringside and Warrior Sculpt, Equinox is recognized for its innovative and expert-designed sessions that challenge and motivate participants.
What role do workout partners play in motivation?
Workout partners, especially those perceived as stronger or more advanced, can significantly enhance motivation during group exercise classes. As evidenced by the 2020 study by Deborah L. Feltz from Michigan State University, training alongside a superior partner or exercise coach can lead to increased effort and performance, emphasizing the motivational benefits of group dynamics in fitness settings.
Who is the exercise coach?
An exercise coach, specifically referred to as a strength and conditioning coach (SCC) in exercise physiology, is a professional trained in optimizing athletes’ performance through tailored training regimes. These coaches typically have formal education in sports science-related fields, with 99% of them holding at least a bachelor’s degree and 71% possessing a strength and conditioning certification.
In a 2022 study by Anthony Weldon from The Technological and Higher Education Institute of Hong Kong, the practices of 156 exercise coaches were surveyed. The results revealed that they commonly use periodization strategies, physical testing, Olympic weightlifting exercises, and plyometric routines.
What does an exercise physiologist do?
An exercise physiologist is a specialized healthcare professional who plays an essential role in interdisciplinary teams for managing noncommunicable chronic diseases. These include conditions such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. Exercise physiologist expertise in clinical exercise interventions and their ability to develop tailored exercise programs make them crucial players in chronic disease management.
What are the main jobs in exercise science?
The main jobs in exercise science include the following.
- Exercise Physiologist
- Strength and Conditioning Coach
- Sports Nutritionist
- Athletic Trainer
- Researcher in Kinesiology
Who are the highest-paid exercise trainers?
The highest-paid exercise trainers in the industry have built strong personal brands and often work with celebrity clients. Among them, Tracy Anderson stands out, having developed the Tracy Anderson Method and trained celebrities like Gwyneth Paltrow, amassing an estimated net worth of $110 million. Kayla Itsines, the Australian creator of the Bikini Body Guide fitness program, has a net worth of around $46 million, while Canadian trainer Harley Pasternak, known for the 5-Factor Diet and his clientele including Rihanna and Halle Berry, boasts a net worth of approximately $25 million.
Which celebrities are known for their workout routines?
This list shows 10 celebrities who are known for their workout routines.
- Jennifer Lopez: Focuses on core strength and uses unique exercises like the downward dog push-up.
- Rihanna: Incorporates running 5ks and Pilates into her exercise routine.
- Olivia Munn: Incorporates martial arts into her daily routine, taking about 30-45 minutes per session.
- Davina McCall: Regularly works out and has her own fitness app called “Own Your Goals” to help others get fit.
- Michelle Keegan: Enjoys fasted HIIT sessions in the morning for the endorphins and quick results.
- Gabrielle Union-Wade: Is dedicated to her gym workouts, frequently incorporating resistance bands, squat racks, and gliders.
- Rebel Wilson: Achieved her Year of Health goals through high-intensity workouts, hiking, battle ropes, tire-flipping, and stair-climbing.
- Gemma Atkinson: Became the celebrity face of #girlswholift after undergoing strength training transformation programs with UP Fitness.
- Jennifer Aniston: Has been practicing yoga since 2005 and credits it for sculpting lean muscle.
- Clara Amfo: Runs regularly, occasionally boxes, and enjoys trying new things like weighted hula hoops in her fitness routine.
Who are the top fitness influencers?
Here are the top 15 fitness influencers from social media like Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok.
- Jen Selter
- Kayla Itsines
- Simeon Panda
- Dannella Munoz
- Lauren Kagan
- Massy Arias
- Emily Skye
- Jeanette Jenkins
- Joe Wicks
- Alexia Clark
- Lauren Fisher
- GrowWithJo
- Shaun T
- Dylan Werner
- Sophie van Oostenbrugge
What are the social exercise trends?
Social exercise trends refer to the evolving patterns and preferences in physical activities influenced by societal changes. These trends reflect the shifts in how people choose to engage in physical fitness, often influenced by factors such as technological advancements, changing lifestyles, and the influence of social media.
HIIT workouts remain popular because of their efficiency and versatility, suitable for both gym and home environments. Wearable technology, such as smartwatches, has become indispensable for tracking various health metrics, enhancing workout efficiency. Simultaneously, there’s a rising emphasis on the therapeutic aspects of exercise, viewing it as a holistic approach to mental and physical well-being.
What are the global exercise trends?
Global exercise trends refer to patterns in physical activity observed in different regions of the world. These patterns may cover the types of physical activities people engage in, the amount of time spent on exercise, the age groups most active, and the changes in these parameters over time.
The global exercise trend is alarmingly skewed towards insufficient physical activity among adolescents, particularly girls. In her 2020 study, Regina Guthold from World Health Organization (WHO) suggests an urgent need for policy action to curb these trends, with data suggesting little progress in reducing levels of insufficient activity from 2001 to 2016.
What stops people from exercising?
Barriers to exercise refer to the factors that prevent individuals from engaging in regular physical activity. These barriers may be psychological, social, environmental, or physical in nature.
According to a 2008 study by James H. Rimmer, the most common barriers to exercise among adults with unilateral stroke were the cost of the program, lack of awareness of a fitness center in their area, lack of transportation to a fitness center, lack of knowledge about how to exercise and where to exercise.
This graph shows the most common barriers to exercise.
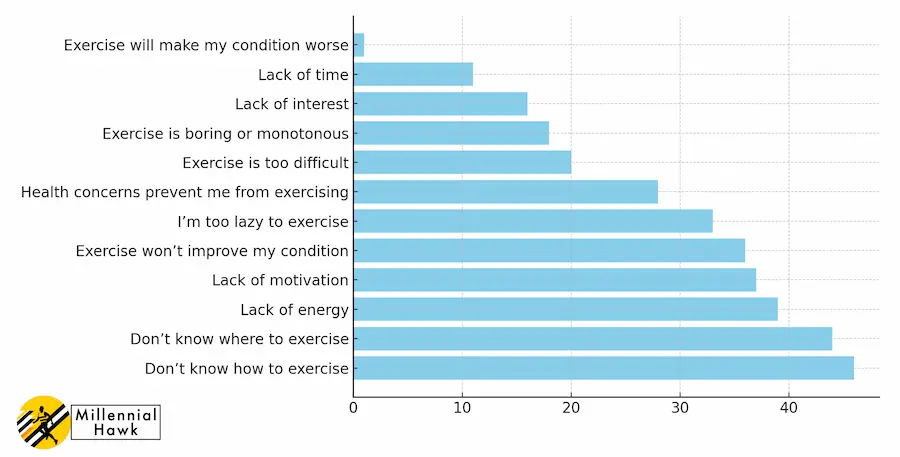
How can one lose weight without exercising?
One can lose weight without exercising by focusing on dietary changes, such as adopting a balanced, calorie-controlled diet rich in whole foods, vegetables, and lean proteins. Another method is through medically supervised interventions, including the use of FDA-approved diet pills or weight loss medications, but these should only be considered after consulting a healthcare professional.
How much exercise is too much?
Exercising too much, or overtraining occurs when there’s an imbalance between training and recovery — when the training intensity and/or volume exceeds the body’s ability to recover. Symptoms of overtraining include persistent fatigue, decreased athletic performance, increased susceptibility to injuries, sleep disturbances, and mood changes. The exact amount of exercise that’s “too much” varies for each individual and depends on factors like fitness level, age, nutrition, stress, sleep, and overall health.
How to start an exercise routine?
Here are 9 ways to start exercising routine after a break.
- Design exercise routine based on your needs
- Get help from a healthcare professional
- Train with a trainer
- Try Workout Apps To Start Exercising
- Identify Your Barriers To Exercise
- Start Exercising Slowly With Lower Intesiity
- Find an Exercise Routine That You Enjoy
- Make It A Habit
- Find a Workout Partner

