In this article, I will be answering one of the most common questions I get about OMAD, which is how much protein should you eat.
In general, on OMAD, you should be eating at least 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. This translates to around 50-60 grams of proteins per day for a sedentary man, and around 40-50 grams of proteins per day for a sedentary woman.
However, depending on other factors, like physical activity, age, lean body mass, and your personal goals, those recommendations will vary. I will also explain the exact process of protein absorption and clarify is it good to eat a lot of protein at once.
OMAD With High Protein Meals
Doing OMAD with high protein meals is important because our body requires proteins on a daily basis, and having high protein meals will ensure optimum body function, proper metabolic functions, maintain lean body mass, and prevent form nutrient deficiencies.
Unlike carbs, proteins are the most essential macronutrients that we need to deliver to the body on a daily basis. For instance, if you don’t eat any carbs, your body will use stored fat as energy instead (source).
No problem. So your body doesn’t really “need” carbs to thrive. They have a lot of benefits, and of course, it’s easy and fast energy for the system, but they are not essential.
But we can survive months and years without them. On the other hand, proteins are essential. This means your body needs a certain amount each day. Once you eat proteins, they’re broken down into amino acids. From there, they enter the “amino acid pool”.
It’s like a waiting room where they stay before they can be used up for all sorts of jobs. And if your diet is lacking in proteins for an extended period of time, this means there are still jobs to be done, but there is nobody in the waiting room.
So, because our body is extremely efficient and adaptable, it will start to catabolize its own tissues to maintain an adequate amount. It will recruit amino acids for the waiting room from lean body mass (aka muscle) (source).
This is called muscle atrophy. You are losing muscle mass. That’s why getting proteins on a daily basis is critical. The main function of proteins is for building and restoring your body tissues. Some of the changes we can see with the naked eye. Think about your nails, hair, and skin.
They all regrow with new cells daily. Others, like enzyme production or hormone production, cannot be seen. According to a number of studies, most people will benefit from more protein in their diet. Here are some of the most common benefits.
Why Enough Protein On OMAD Is Important?
You need enough proteins on OMAD because it is essential for your cardiovascular health, helps you recover faster, helps with your appetite control, essential for maintaining lean body mass (muscle), helps to improve your immune system, and keeps your satiety high.
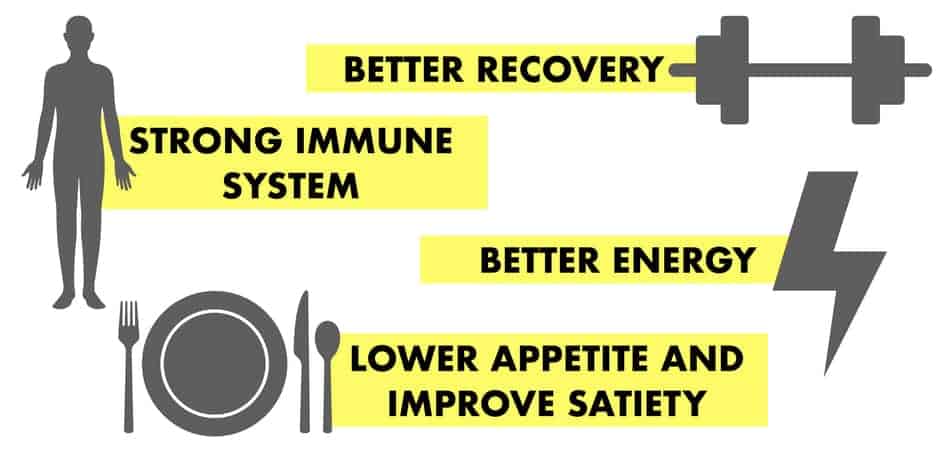
- They help you with appetite control. A high-protein diet leads to improved satiety signals. This means you are less hungry when you eat more proteins.
- They improve your cardiometabolic health. High protein diets can help lower blood pressure, improve glucose levels, cholesterol, and more. That is because they don’t affect insulin as much as carbs do. So when you eat more proteins, you can maintain your sugar levels better (source).
- They improve your immune system. Proteins are the building blocks of antibodies, like white blood cells, and are responsible for several functions in the immune system. This means they protect from many bacterial infections.
- They can help you recover faster. A higher amount of protein can help with repairing tissue after exercise and after an injury. That’s why athletes who are injured, have higher recommendations for proteins (source).
- Apart from regrowing the cells, proteins are also essential for maintaining muscle mass. This translates to better strength, muscle growth, faster weight loss, and easier body composition management. The more muscle mass you have, the more proteins you need to maintain it.
It’s like having a farm full of animals. The more animals you have, the more food you need to feed them.
So muscle is not only a emergency storage of amino acids (you don’t want that to happen) but it’s also a farm of tissues that require proteins each day.
In other words, muscle is expensive. And the more muscle you have, the more proteins require to “stay active”.
How Much Protein Can Be Absorbed On OMAD?
There is no upper limit to protein absorptions from a single OMAD meal. Some publications show that only 20-30g of protein can be fully absorbed. However, these data involve only fast-digesting proteins, without taking into consideration of slow-digesting proteins.
In other words, doesn’t matter if you have one meal a day or 3-4 small meals (source). OMAD will have the same protein absorption as eating regular meals.
You absorb the same amount of proteins, regardless of the meal frequency. If you’re eating just regular food that has proteins (meat, eggs, plants) those have slow digestive proteins, therefore it will take a long time to break, digest, and absorb.

On the other hand, if you want to maximize muscle protein synthesis to build muscle, your goal is to deliver 20-30g of fast-digesting proteins every 3-4 hours for a maximal anabolic response. Anything more than that won’t make any difference in muscle protein synthesis (source).
Muscle Protein Synthesis On OMAD
When doing OMAD is important to pay attention to, and remember about muscle protein synthesis. People who are physically active people, and who want to gain muscle while doing OMAD need around 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight daily.
The process of building and maintaining muscle mass is called muscle protein synthesis. The process of losing muscle is called muscle protein breakdown.
The more muscle you have, not only it require more protein, but it also requires more calories.
Imagine two people having the same weight. 150 pounds. Their scale shows the same number, but person A is lean, has more muscle than fat. And person B has more fat than muscle.
Now imagine those two people go for a 2 mile walk. The same distance, the same pace.
Person A, who has more muscle, will use more muscle to move. And because muscle is expensive to move, it will cost him a lot of energy. This means during this 2 mile walk he will burn lot’s of calories.
On the other hand, person B who has less muscle and more fat, even if he walks the same distance at the same pace as person A, will not use that much energy because he doesn’t have much of a muscle mass.
That is the most important thing you must remember when doing OMAD. The more lean body mass you have, the easier it will be to lose and maintain weight.
When you are eating 3 meals a day, and each meal contains some amount of proteins, there is no need to worry about it.
However, when you’re doing only one meal a day for an extended period of time (3-6 months), and you want to keep your muscle mass on, you should start to prioritize (source).
It doesn’t mean you have to stress about planning your meals, but you want to include a good amount of proteins in your meal.
Where Can You Get Your Proteins From?
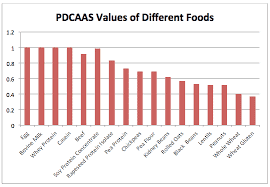
Protein quality is determined by the amino acid number and protein digestibility aka bioavailability.
PDCAAS (Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score) is the gold standard to measure protein quality. It measures the number of essential amino acids found in the smallest quantity in a particular food.
Proteins are omnipresent in many animal-based foods and plant-based food. However, the best protein sources are those that can deliver all essential amino acids.
Animal protein contain all essential amino acids, thats why they rank the highest on the protein measures above plants.
It doesn’t mean that protein from plant-based proteins are worst or better from animal-based protein. It means that to get same make-up of full available EAA we must continue combine food sources from variety of plants on a daily basis.
There are 20 main amino acids.
If you’re having an animal-based food like meat, eggs and fish, those types of food sources contain all of the essential amino acids.
If you’re having a plant-based food source, like tofu, peas, nuts, beans, or chickpeas, you must eat more variety of that food because they do not contain all of the essential amino acids.
For instance, to get your daily proteins from beef, all you need is a 10oz steak and you’re covered. Not only it contains enough proteins, but it also has all the essential amino acids.

But on the other hand, to get the same amount of proteins from plants, with the same amino acid ratios, you need to combine more variety of food. This means your one meal a day will have to be composed of legumes, lentils, peas, etc.
So you have to eat more food, and constantly changing the variety to achieve the complete amino acid profile.
Go Further with OMAD
This article is part of the OMAD: What To Eat To Stay Full For Longer
In the following articles, I show you all the related aspects necessary to get started with OMAD and knowing what to eat for the best results.
Learn More: Click here to learn more about can you snack on omad