One of the most effective ways to lose weight is to create a calorie deficit where you eat less food than your body needs. Eating below BMR is a viable way to create that energy deficit (as long as you like to count calories).
Today I will explain if it’s safe to eat below BMR and what happens to the body if you do it for a long period of time.

In general, you should be eating around or under your BMR to lose weight because it creates 30% of a calorie deficit, which can trigger weight loss as long as you maintain enough consistency. However, the longer you eat below your BMR, your metabolism can slow down and you can lose some muscle mass.
This is my brief answer, but if you wanna know more details about how effective is to eat below BMR for weight loss, how to do it correctly, and what are the potential disadvantages, keep reading.
Can I eat below my BMR to lose weight?
As a whole, you can eat below your BMR to lose weight because it will create a negative energy balance. This way your body uses stored fat as an energy source and over time reduces excess weight.
However, this approach should be used with caution becasue prolonged calorie deficit may lead to muscle loss, and energy drop, and over time can slow down the metabolic rate.
In other words, eating below your BMR should only be used as a tool that is done intermittently (e.g. 1-2 months), not as a long-term lifestyle practice.
What does it mean to eat below your BMR?
According to Wikipedia, BMR (basal metabolic rate) is the rate of energy expenditure per unit of time at rest. In simple terms, it’s the number of calories that the body uses every day for basic metabolic functions like breathing, blood flow, or cognitive functions.
Basal metabolic rate gives your body energy to be able to maintain things like:
- Blood circulation
- Breathing and oxygen transport
- Cellular signaling
- Protein synthesis
- Cognitive processes
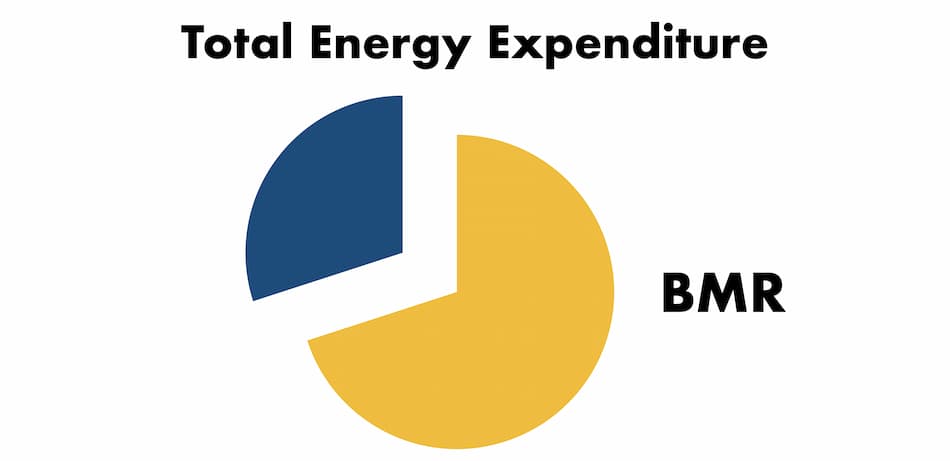
It contributes to 70% of your total energy expenditure (source). For example, if your total energy expenditure is 2,500 kcal, your BMR would be around 1750 kcal (70% of the total).
Eating below your BMR means consuming less food that is required to cover all the energy costs of the body.
It’s fair to say that eating below your BMR almost guarantees you’re in a calorie deficit. Also remember that apart from weight loss, negative energy balance will create other metabolic adaptations (more on that later).
This may not come as a surprise to you, but from all your BMR, the most “calorie expensive” is lean muscle mass.
Muscle mass not only requires more nutrients but also more oxygen. And with more oxygen consumed, you burn more calories.
(Which is why is super important to eat high protein and do strength training during your calorie restriction).
Is it ok to eat below BMR? On the one hand, it is ok to eat below your BMR for weight loss becasue it helps to improve insulin sensitivity and lower hunger. On the other hand, eating less than your BMR for too long without supervision and a correct diet plan can contribute to nutrient deficiency.
Is It safe to eat under your BMR?
To be honest, there are not many long-term studies on humans who were willing to eat less than their BMR. Most of the available research is made on rodents. Most of the calorie restriction studies were done for a short period of time.
There are a small number of individuals who were eating calories below their BMR for a number of years. This means that little is known regarding the long-term effects of caloric restriction.
However.
According to Luigi Fontana, MD, Ph.D., a research professor from the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, people who were eating below BMR for 12 months (between 1,100-1,900 kcal/day) managed not only to reduce their BMI, but also noticed significant improvements in LDL-C, HDL-C, triglycerides, and blood pressure.
People who managed to eat below BMR for an extended period of time also improved their insulin sensitivity, and reduced inflammation, as reflected in extremely low CRP levels, said Dr. Fontana (source).
NOTE: Please keep in mind that people from this study consumed a large number of proteins (around 26%). They eat a wide variety of nuts, dairy products, egg whites, wheat, soy proteins, meat as well as vegetables and fruits.
High protein intake stimulates muscle protein synthesis, and if you combined that with resistance training, it can help you to maintain muscle mass, even when eating below your BMR.
Is it dangerous to eat below your BMR? In general, it is safe to eat under your BMR as long as you consume a balanced diet made of protein, carbs, fats, and all vitamins and minerals. Lowering your calorie intake to below BMR level is nothing different than calorie restriction or intermittent fasting.
How to eat below BMR?
Calculate your BMR
The first step to start eating below your BMR is to calculate your basal metabolic rate.
Knowing the estimated amount of calories that need to consume creates a negative energy balance. Knowing your BMR can give you an idea of how many calories a day you need to eat to lose weight.
Normally, you can only accurately measure your BMR by either:
- Direct calorimetry
- Indirect calorimetry
Both of those methods are ridiculously accurate but require a strict laboratory setting and professional air-tight chamber to measure the heat produced by the body and the rate of oxygen exchange (source).
However.
None of those methods are widely available or practical. So we have to rely on estimates and predictive equations. Those types of BMR calculators aren’t as precise as calorimetry (even up to 20-30% off) but they are good enough to guess less the number of calories.
Measure your food potions
Once you know your BMR, the next step is to measure your food potions and calculate the calories in your meals. The goal here is to stay around or just under your BMR.
For example, if your BMR is 1750 kcal, your goal is to consume 1750 kcal per day or less. I recommend having at least 30% of your calories from lean protein sources like meats, eggs, fish, and dairy.
Resistance Training
Doing weight training while being in a calorie deficit can help not only with weight loss, but it will also help to maintaining your results. I recommend doing something like full-body strength training where you hit all major muscle groups.
Eat below BMR or TDEE?
In general, you want to eat below your BMR, not TDEE. Eating below BMR will more likely create a calorie deficit. Total daily energy expenditure (TDEE) is the total amount of calories used by the body and this equation is calculated by the estimates that can be off by 20-30%.
In other words:
- Eating below TDEE may or may not put you in the calorie deficit
- Eating below BMR will definitely put you in the calorie deficit
What happens if I eat under my BMR?
Initially, when you eat under your BMR, your body will start to use fat for energy and cause weight loss. However, over time, the longer you stay in the calorie deficit, the body will undergo metabolic adaptations and the rate of weight loss will drop.
After you already lost a significant amount of weight, the body will respond with lower energy expenditure. This means you won’t burn as many calories as before the weight loss (source).
That happens because:
- You will eat less food so your thermogenic effect of food will decrease
- You have less weight so your body will use less energy to move around
- You have less lean mass so you will consume less oxygen (unless you do strength training)
Will I lose weight if I eat below my BMR?
On average, you will lose weight if you eat below your BMR. Eating below your basal metabolic rate will cause the body to switch from using external sources of energy (food from the last meal) to using internal sources of energy (stored body fat).
Depending on your weight loss goal, this process can take several weeks or even months. And with a properly designed nutrition plan and regular resistance training, you can not only have better results but also keep on burning calories, without the weight loss plateau.
Adding strength training to your routine can not only help you with adding more energy to the tank but also it can improve your:
- Insulin sensitivity (active muscles soak up the glucose from the blood like a dry sponge).
- Resting metabolic rate (adding more lean mass will ensure you continue to burn more calories despite calorie deficit).
- Glucose metabolism (more glucose will be converted to glycogen).
- Blood pressure (studies show that strength training can decrease blood pressure and perhaps the risk of future CVD development) (source).
- Body fat (more lean mass burns more calories so it will enhance the calorie restriction).
- Gastrointestinal transit time (strength training can accelerate bowel transit time, especially in previously sedentary people) (source).
What happens if you eat below your BMR and work out
Initially, eating too few calories and working out can help you speed up the process. Low-intensity exercise can suppress your appetite and lower your hunger. However, after a period of time, too much of a calorie deficit can decrease your performance and your energy levels.
It will all depend on your goals.
- If you love to exercise, increase your calorie intake.
- If you don’t exercise regularly, lower your calorie intake.
You don’t want to overdo your calorie restriction and exercise at the same time. Going too fat too soon can lower performance, and halt progress. Your goal is to keep it sustainable.
The Formula 1 car can go ultra-fast, but it can’t go 5000 miles over several years like a family Honda Accord. Your goal is long-term success, not overnight juice cleanse.
NOTE: For people who struggle with exercise while on a diet, it is much more realistic to improve their NEAT (non-exercise activity thermogenesis).
NEAT is everything that you do during the day. Everything.
- Fidgeting
- Walking
- Gardening
- Maintenance of posture
- Leisure activities
- Playing guitar
- Shopping
You would be surprised how many calories can be burned if your all day is filled up with just general being-busy activities. The more you move, the more calories you will use.
Does Eating Below BMR Slow Metabolism?
In general, eating below BMR will slow down metabolism. After significant weight loss, the body will start to adapt by lowering the resting metabolic rate, creating changes in thyroid and reproductive hormones (reducing testosterone), and lowering the thermic effect of food.
In other words, you hit the weight loss plateau.
When you chronically restrict your body from food, it will start to down-regulate certain mechanisms to survive. This of course will lead to lower energy, a weaker immune system, mood disruptions, and stress.
The easy way to overcome that is by doing calorie cycling.
Calorie cycling helps you to alternate your calorie deficit days with normal eating days. It will “trick” the body and prevent it from plateauing.
The easiest way to do so is to have 1-2 days per week of eating normal (maintenance level) calories and 5-6 days of calorie deficit when you eat below your BMR.
So, should you eat less than your BMR to lose weight?
As a general rule, you can eat less than your BMR to lose weight. Lowering calories under your basal metabolic rate will put you in a negative energy balance where calorie expenditure exceeds calorie intake.
This creates a calorie deficit where the body burns fat for energy.
However, being in deficit for too long without enough protein and resistance training can slow down your metabolic rate.
So if your goal is to lose fat and get a diced look where your abs never go away, you need to cycle your calorie intake and hit the gym 3 times per week.
Conclusion
You can eat below your BMR as long as you have a well-balanced diet.
Adding extra strength training and prioritizing protein intake will help you to maintain lean mass and make sure you’re losing fat, not muscle.
After a prolonged dieting period, it is expected to hit the weight loss plateau. To overcome that start doing calorie cycling by alternating normal eating days with dieting days.
